Vesting plays a key role in tokenomics, helping stabilize token prices and align long-term interests. It’s a strategic way to lock up tokens for team members, investors, and advisors—ensuring loyalty while preventing sudden market dumps. In this article, we’ll break down how vesting works, the different types, real examples, and current trends.
How does a crypto vesting schedule work
The crypto vesting schedule has predefined conditions that determine when and how holders of cryptocurrency tokens receive ownership over assets, and the possibility to sell and transfer them. Vesting schedules encourage loyalty and performance by ensuring that members receive the full benefits of their total rewards over time.
The main goals of crypto vesting schedules are:
- Motivation of participants to long-term obligations: deferred full access to assets, encourages people to stay in the project and fulfill certain requirements to achieve the company’s success.
- Stabilization of the tokens cost: Vesting on a certain schedule distributes sales over time. This prevents abrupt sales and possible price destabilization.
- Investor protection: Company employees are unable to sell their tokens immediately after a public sale.
Best practices for structuring your vesting schedule
The structure of the schedule may vary depending on the duration of the vesting period, the cliff periods (if any), and the frequency of vesting events.
- Duration of vesting: The time required for token transfers varies by agreement but typically ranges from 1 to 4 years.
- Cliff period: the pause period between the start of vesting and the first payment of tokens after unlocking. It can take months or even a full year.
- Vesting frequency: After a break, tokens can vest monthly, quarterly, or annually.
The vesting period can begin after a cliff, or it can start immediately at the token launch during the Token Generation Event (TGE).
Different vesting designs
There are main types of vesting schedules:
Linear vesting
This vesting type assumes linear unlocking of tokens in volume and time, the indicators of which are proportional. For example, a company can set free 10% of all locked-up tokens every six months during the vesting period.
Graded vesting
Graded vesting allows for the gradual release of tokens over a particular number of years or months. For example, a company might release 25% of the coins within the first eight months, followed by another 35% in the second year. The remaining 40% will be released in the third year.
Cliff-vesting
In this case, the start date of the vesting procedure is determined, and the cliff is the selected period for blocking tokens. Accordingly, the investors will receive their share of crypto assets after storing liquidity within the project for a certain time. Upon expiration, tokens will be distributed through linear or graded vesting.
Immediate vesting
This type means that participants get access to their benefits in full without any delay or predetermined waiting period.
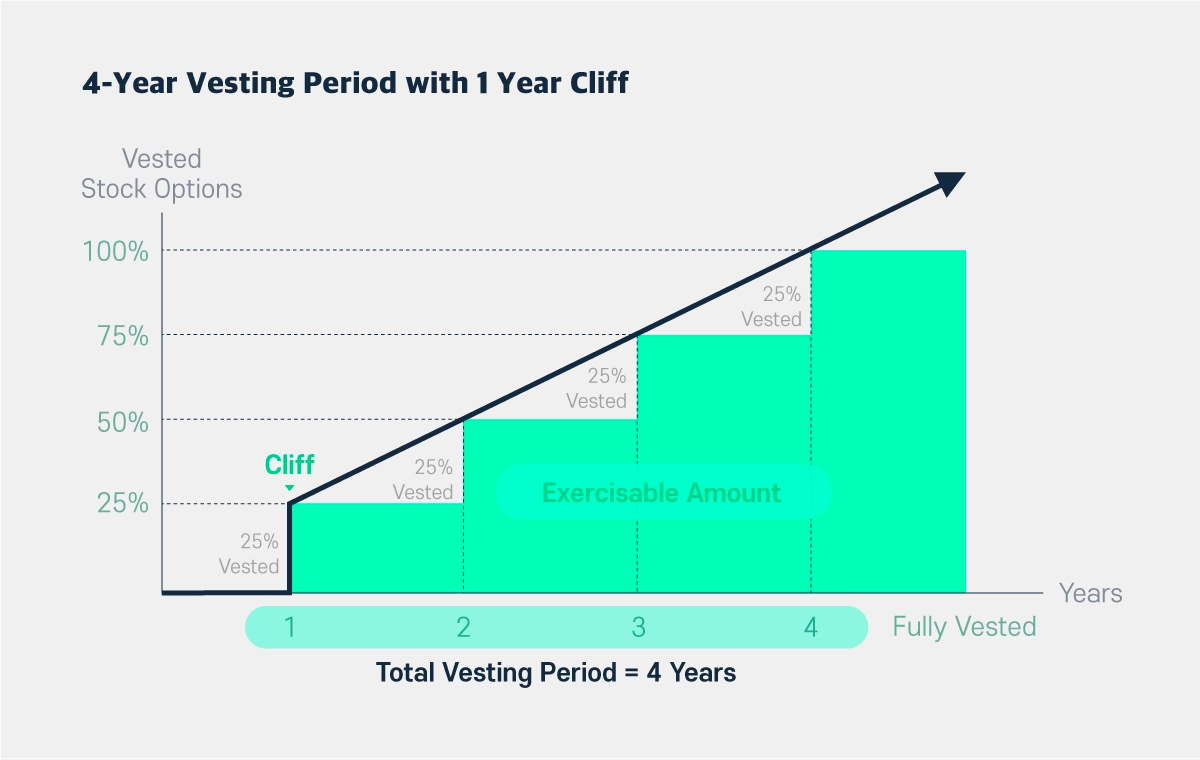
Understanding the 4-year vesting model: why is it popular
Focused on on long-term prospects for the project the 4-year vesting model is popular among many crypto companies. Payments happen every year — it is a cliff period. Moreover, if a participant leaves the project earlier than a year later, they do not receive anything. After this annual period, a quarter of the total grants are transferred, and then the transfer of rights occurs monthly.
Example of a 4-year vesting schedule with a 1-year cliff period:
Growing popularity of 1-year vesting models
Recently, companies have been choosing a 1-year vesting model. While the traditional 4-year vesting focuses on long-term stability, this newer and briefer opportunity offers more flexibility, adaptability, and requires participants to give results faster. This short-term model balances rapid liquidity and continued commitment. In turn, a chance to gain profit in a shorter time attracts specialists who are not afraid of intense workflow.
Differences between traditional and accelerated vesting models:
Traditional model:
- typically has a four-year vesting period,
- one-year cliff,
- ensure gradual equity distribution,
- encourage long-term employment.
Accelerated model:
- has a one-year vesting schedule,
- offers immediate equity realization,
- can be advantageous for recruitment but may pose challenges for long-term retention
Case studies
How effective is Coinbase’s 1-year vesting approach
Coinbase switched to a 1-year vesting model in 2021. Adopting such a structure, the company outlined rather strict restrictions for employees. This meant that the number of assets they received would vary depending on whether the price of the assets was rising or falling.
However, this measure was effective in achieving rapid project success and retaining specialists. After analyzing the effectiveness of the 1-year vesting approach, the company noted fewer cases of early exit after vesting.
Lyft and Stripe's 1-year vesting strategies in 2021
In 2021, Lyft and Stripe analyzed the prospects for vesting within the annual period.
According to Stripe’s vesting scenario, new team members get all their assets after a year of work. Subsequent equity awards vest at 25% over 12 months.
With Stripe's equity vesting strategy, new employees get 25% of the yearly grant every three months, while the executive leadership team will remain on the four-year schedule. This step to 1-year vesting schedule was made by Lyft to balance the compensations and make it consistent for existing employees and new hires after the price swing of the company’s shares.
The change from the traditional approach to the accelerated one aimed to enhance talent acquisition and retention by providing quicker access to equity, making compensation packages more attractive in a competitive labor market. Both companies noted increased engagement with stakeholders, and the accelerated vesting model complemented their development paths.
Key advantages of 1-year vesting structures
Quick result. Tight deadlines motivate stakeholders to engage intensively and achieve vigorous results.
Flexibility and adaptability. The shortened vesting model allows them to adapt to changing market realities quickly.
Attracting talent. Highly qualified specialists are interested in obtaining rapid-time benefits and remain committed to the project until the end of the vesting period.
Potential drawbacks of adopting a 1-year vesting plan
Short-term perspective. Project participants can only be interested in obtaining quick benefits, and not in the long-term success of the project.
Quick rollback. After receiving all the powers, the participants can throw the project, which in turn will lead to a decline.
Real-world vesting schedule examples
Arbitrum
Vesting design: 36-month linear model + immediate vesting
Cliff-period: 1 year
The Arbitrum platform distributes its ARB tokens into five categories: investors, team, DAO treasury, DAO ecosystem and individual wallets. The team and investors receive their tokens on a linear schedule: they receive rights to part of the tokens every month over 36 months. Tokens for individual wallets and the DAO ecosystem were fully released in TGE, without an entitlement or cliff period. This means that holders received their full amount of assets when the token was launched, allowing them to trade them freely without any time restrictions.
Polkadot
Vesting design: 6-year linear model
Cliff-period: 1 year
A multiple blockchain Polkadot assigned half of its DOT tokens to the Web3 Foundation, which is responsible for its development and maintenance. These tokens adhere to a 6-year vesting schedule with a one-year cliff period, meaning the team cannot sell any tokens during the initial year and then gains access to 16.67% each month for five years.
Axie Infinity
Vesting design: 3-year linear model
Cliff-period: 1 year
Axie Infinity game allocated 90% of its AXS tokens to a community treasury. The tokens are tied to a 3-year vesting schedule with a one-year cliff. After that, the team can release 33.33% of the tokens each month for the following two years.
Streamflow overview and its role in token vesting
Streamflow is a user-friendly service designed to streamline the process of creating and distributing personal tokens. The platform efficiently handles all aspects of token management, from airdrops to mining.
Streamflow allows users to configure fully automatic vesting schedules. The ecosystem will immediately unlock tokens for customers and transfer tokens to the wallets of their recipients.
The platform has three levels for smooth token management:
- Basic level. The protocol level consists of a set of smart contracts on first-level blockchains such as Solana, Aptos, and Sui.
- Infrastructure level. Provides a variety of software development kits and application programming interfaces (APIs).
- The business level is the user level. It consists of handy buttons and menus that users can click on to control various decentralized token management tools.
Conclusion
In general, vesting schedules are quite an important tool for studying tokenomics. It will be difficult for investors or potential team members to understand the overall project plan if the project does not have a clearly defined investing plan.
The vesting schedule models we reviewed have their own pros and cons. Therefore, each project chooses the most suitable type of vesting, based on the goals and priorities of the company.
A balanced token vesting schedule manages price fluctuations and overall project integrity. The schedule ensures long-term commitment and strategic financial decisions for the company and investors.
FAQ
What is a vesting schedule?
The crypto vesting schedule is a schedule that determines when and how holders of cryptocurrency tokens obtain ownership of these assets, sell them, and transfer them.
Grant date vs vesting commencement date?
The grant date is the date when tokens are awarded or provided to the interested party. The vesting commencement date is the starting point for the vesting schedule. The individual begins to accumulate property rights over time.
What are token vesting trends?
The crypto community is divided: some choose short vesting periods for agility, others longer ones for long-term prospects and commitment.




